Tags
802.11 Control Frames assist with the delivery of Data & Management frames. Unlike management & data frames, Control frames does not have a frame body.
 The type (always 1 for control frames) & subtype fields identify the function of a frame. So below figure shows the different type of control frames.
The type (always 1 for control frames) & subtype fields identify the function of a frame. So below figure shows the different type of control frames.
 Here is a brief description of each type of Control Frame & how you can filter them in wireshark.
Here is a brief description of each type of Control Frame & how you can filter them in wireshark.
1. Control Wrapper
The Control Wrapper is used to carry any other control frame, other than another Control Wrapper frame together with HT Control field (in 802.11n). You can filter them on wireshark using below display filter.
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 7)
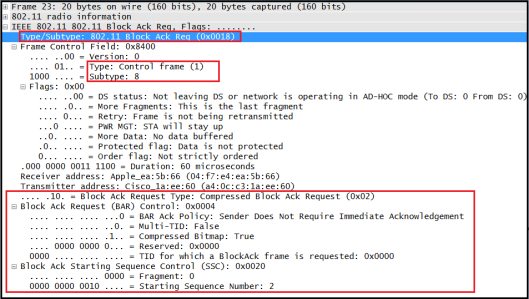
 2. Block Ack Request (BAR)
2. Block Ack Request (BAR)
When a station intend to use Block ACK mechanism to transmit QoS data, it first check to see whether the peer station is capable of Block ACK. Then send block of QoS data frames & requesting all QoS data frame to ACK by sending Block ACK Request (BAR) to receiving station. Here is the wireshark filter you can use.
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 8)
 3. Block Ack
3. Block Ack
This is used to Acknowledge a block of QoS data frames instead of acknowledge each unicast frame independently. Here is the wireshark filter you can use to idnetify Block Ack from a given capture.
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 9)
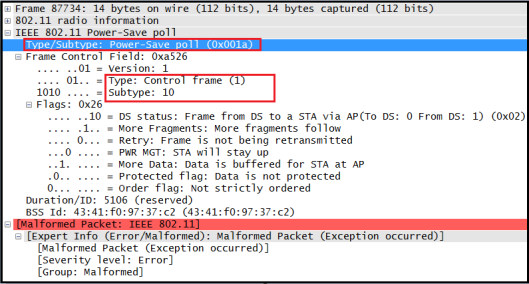
 4. PS-Poll (Power Save-Poll)
4. PS-Poll (Power Save-Poll)
When station receives beacon, it checks to see its AID (Association ID) in that to see any buffered unicast data frame to that station. If so station remain awake & send a PS-Poll frame to the AP. When AP receives PS-Poll frame, it wil send the buffered unicast frame to the station. Here is the wireshark filter & sample PS-Poll frame (note that due to bad FCS it identified as malformed packet)
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 10)
 5. RTS – Request to Send
5. RTS – Request to Send
RTS/CTS is a mechanism that perform a NAV (Network Allocation Vector) distribution and helps prevent collision from occurring. When this enabled, everytime a station wants to send a frame, it must perform RTS/CTS exchange prior to normal data transmission. Duration of RTS frame specify how much time it require for the data transmission (so listening station set their NAV timers to this value)
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 11)
 6. CTS- Clear to Send
6. CTS- Clear to Send
When a tranmitting station send RTS, the receiving device (typically AP) should send CTS control frame. Using below wireshark display filter you can see CTS control frame in a capture.
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 12)
 7. ACK
7. ACK
Since 802.11 stations are not able to Tx & Rx at the same time, to ensure a transmitted unicast frame delivered correctly it is expected an “ACK” from receiving station. You can filter ACK frame in wireshark using below display filter.
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 13)
 8. CF-End (Contention Free-End)
8. CF-End (Contention Free-End)
Contention Free-End control frame is to indicate to indicate contention-free period in PCF medium access method. You can use below wireshark filter to identify them (Note in this capture there was a CRC error, hence it shown as malformed packet)
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 14)
 9. CF-End & CF-ACK
9. CF-End & CF-ACK
Contention Free-End + Contention Free-ACK (CF-End + CF-ACK) is used to indicate the end of a contention-free period and acknowledge receipt of a frame normally used in when Point Coordination Function (PCF) medium access. You can filter those frame using below display filter.
(wlan.fc.type == 1)&&(wlan.fc.subtype == 15)

References
1. CWAP Official Study Guide – Chapter 5

Very interesting:
Your RTS frame request a duration = 128 microseconds. The access point gives a CTS duration = 84 = 128 – 44 microseconds. It is the same with my access point.
same thing I am looking for, I am not able to understand the value in CTS (duration ID).
what is meant for ?
Hi Saurabh,
The duration value is CTS frame is useful to update NAV timers of listening stations which are connected to AP in the same BSS before accessing the medium for their data transmission .
One more thing , CTS frames are sent @low data rates , so that every stations(including long distance and hidden stations)can hear CTS and adjust their NAV timer
RTS= 3xSIFS + DATA + CTS + ACK =128 usec
CTS=2xSIFS + DATA + ACK = 84 usec
Hope this helps
Isn’t PCF not deployed in AP? Why is still CF-End frame?
You are right, PCF has not implemented. I think those are malformed packet & wireshark wrongly classify as CF-End frames.
HTH
Rasika
The answer below is from CWAP practice test. It says “With the exception of CF-End ”
Not sure where CF-End is used !
Contention free frames (CF) would be used with Point Coordination Function (PCF) mode if it was ever implemented. This contention free mode was designated as optional in the original 802.11 standard. With the exception of CF-End these frames are usually attributed to a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) error which will be identified in the radiotap header in the frame that was misinterpreted by the protocol analyzer.