Tags
In this post we will go through 4-Way Handshake process. This is described in Chapter 5 of CWSP Official Study Guide. Page 194 of this book shows the below RSN key hierarchy. Also watch this CWNP video for more detail about this key hierarchy.
 MSK-Master Session Key ( or AAA Key):
MSK-Master Session Key ( or AAA Key):
Key information that is jointly negotiated between the Supplicant & Authentication Server. This key information is transported via a secure channel from Authenticating Server to Authenticator.
PMK-Pairwise Master Key:
PMK is derived from MSK seeding material. PMK is first 256bits (0-255) of MSK. It can be derived from an EAP method or directly from a PresharedKey(PSK).
GMK-Group Master Key:
GMK is randomly created on Authenticator & refresh it in configured time interval to reduce the risk of GMK being compromised.
PTK-Pairwise Transient Key:
A value derived from PMK,Authenicator nonce(Anonce),Supplicant nonce(Snonce), Authenticator Address, Supplicant Address. This is used to encrypt all unicast transmission between client & an AP. PTK consist of 5 different keys
1. KCK-Key Confirmation Key-used to provide data integrity during 4 -Way Handshake & Group Key Handshake.
2. KEK – Key Encryption Key– used by EAPOL-Key frames to provide data privacy during 4-Way Handshake & Group Key Handshake.
3. Temporal Key – used to encrypt & decrypt MSDU of 802.11 data frames between supplicant & authenticator
4. Temporal MIC-1
5. Temporal MIC-2
GTK-Group Temporal Key:
GTK is used to encrypt all broadcast/multicast transmission between an AP & multiple client statsions. GTK is derived on Authenticator & sending to supplicant during 4-Way Handshake (M3)
4-Way handshake utilizing EAPOL-Key frames initiated by the Authenticator to do the following.
1. Confirm that live peer holds PMK
2. Confirm that PMK is current.
3. Derive a fresh PTK from PMK & Install the pairwise encryption & integrity keys into 802.11
4. Transport the GTK & GTK sequence number from Authenticator to Supplicant & install them in Supplicant & AP(if not already installed)
5. Confirm cipher suite selection.
If it is PSK, 4 way handshak starts immediately after Open System Authentication & Association state finish as you can see below.
 If it is 802.1X/EAP, then 4 way handshake starts when EAP Authentication finished.
If it is 802.1X/EAP, then 4 way handshake starts when EAP Authentication finished.
 Below figure shows the steps involved in 4-Way handshake process. This CWNP video explain well this process & have a look on it before go into details.
Below figure shows the steps involved in 4-Way handshake process. This CWNP video explain well this process & have a look on it before go into details.
 Here is the details about each step. You can filter EAPOL-Key messages using “eapol.keydes.type == 2” wireshark display filter.
Here is the details about each step. You can filter EAPOL-Key messages using “eapol.keydes.type == 2” wireshark display filter.
Message 1 (M1)
* Authenticator sends EAPOL-Key frame containing an ANonce(Authenticator nonce) to supplicant.
* With this information, supplicant have all necessary input to generate PTK using pseudo-random function(PRF)
 Message 2 (M2)
Message 2 (M2)
* Supplicant sends an EAPOL-Key frame containing SNonce to the Authenticator.
* Now authenticator has all the inputs to create PTK.
* Supplicant also sent RSN IE capabilities to Authenticator & MIC
* Authenticator derive PTK & validate the MIC as well.
 Message 3 (M3)
Message 3 (M3)
* If necessary, Authenticator will derive GTK from GMK.
* Authenticator sends EAPOL-Key frame containing ANonce, RSN-IE & a MIC.
* GTK will be delivered (encrypted with PTK) to supplicant.
* Message to supplicant to install temporal keys.
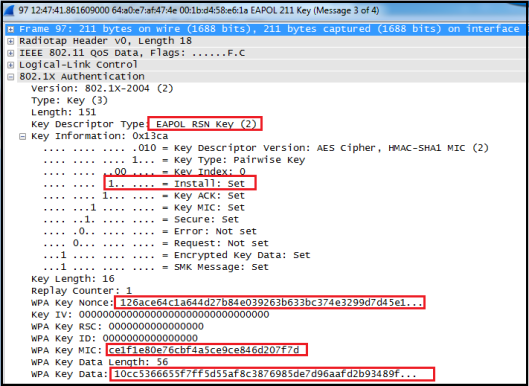 Message 4 (M4)
Message 4 (M4)
* Supplicant sends final EAPOL-Key frame to authenticator to confirm temporal keys have been installed.
 From this point onwards data frame MSDU will be encrypted using PTK or GTK (depending upon unicast or multicast/broadcast frame)
From this point onwards data frame MSDU will be encrypted using PTK or GTK (depending upon unicast or multicast/broadcast frame)
References
1. WPA2-PSK-Final -Sample Packet Capture (Frame 93-99 shows M1-M4 EAPOL-key frames)
2. CWSP Official Study Guide
3. http://www.my80211.com/cwsp-george-stefanick/
4. 802.11i AKM CWNP- White Paper
Related Post
1. CWSP – L2 Encryption Method:WEP
2. CWSP – L2 Encryption Method:CCMP
3. CWSP – L2 Encryption Method:TKIP
4. CWSP – RSN Information Element
5.
6.

Very interesting article, again thank you for your job.
Glad to see my study notes helping many others…
Thanks for the feedback as well.
Rasika
How would you filter for GTK Group Message(2-way handshake) packets that occur after the EAPOL 4-way handshake completes. Lets say that I set the renewal interval to 3 mins, I do see them when i use the EAPOL filter but how do I ONLY see the GTK group messages without the EAPOL frames?
Hi
These frame should be identical to M3 & M4, so I do not think you can filter those GTK group messages separately.
HTH
Rasika
1. For 802.1X, Why M1 have RSNIE, which contains PMKID, what is the use of RSNIE in M1, As in PSK case the data length is 0, so no RSNIE is sent. Plz explain ?
2. Why M2 Msg have RSNIE, what is the use of this RSNIE, for both 802.1X and PSK ?
I think there must be some good reason for this but i am not able to get it.
nayarasi,
Can you please reply to my question ???
Hi Pawan,
I do not know exact reasoning behind it. Hopefully someone who knows will see your question and provide you an update.
Rasika
I just verified this in a capture. If AP sends PMK to the client over the air, then is it not a vulnerability?
PMK is the only hidden component in 4way handshake as for as i have understood. If that is compromised, an attacker can generate the keys using PMK and ANONCE, SNONCE, MAC addresses (which are all sent as plain test)
Hi Shyam,
PMK is never shared by client or authenticator over the air. Only PMKID is an PMK identifier that is used by the entities to check for the cached PMK with respect to pariticular PMKID. PMKID is the unique key identifier used by the AP to keep track of the PMK being used for the client. PMKID is a derivative of AP MAC, Client MAC, PMK and PMK Name.
I hope this clarifies your query.
Hi Pawan Pant,
The RSNIE would be available in M1 only in case of PMKID cached i.e possibility of roaming. Hence it indicates the cached PMKID and count.
The RSNIE is sent in M2 to inform the STA regarding the group cipher suite as well pairwise cipher suite used i.e if AES is used for PTK+GTK for WPA2 only; and the information of AKM suite used. This is also at times tagged as vendor specific.
That’s correct. Just in case of transition the RSN capabilities should be known to target AP as well.
Please explain more about Master Session Key….
Have you gone through this as it explain this topic in detail.
Click to access 802-11i_key_management.pdf
HTH
Rasika
really good
Thanks
Thanks for diagrams and explanations, also references to good material for further reading.
you are guru in wireless – in short with in my team we all call you as “guruvu garu” in telugu language!
Thanks for kind words Santhosh
With some client authentication I can independently capture all 4 messages, but some other clients only 2 or 3 of the 4 messages…why might this be? Is it just a wifi capture problem or is there some other explanation? Also, would a M4 with zero key length be a problem when pmf is required? Thank you for all your work!
Pingback: Wireless Penetration Testing Checklist - A Detailed Cheat sheet - GBHackers On Security
Really want to thank you people on bring up the content togather.. it’s really helpful.
Thank you Amit
Can you reply on my question?
Pingback: Wireless Penetration Testing Checklist – A Detailed Cheat sheet – marktugbo.com
Pingback: Wireless 802.1X – Part 1 | WiFi Ty
Hii Rasika,
In a Light weight setup,
1. where does the GMK is generated? (in WLC or in AP or in RADIUS server)
2. where does the GTK is derived? (in WLC or in AP)
3. where does the PTK and GTK are installed? (in WLC or in AP)
& from where the 802.1x port block occours? in AP or in WLC?
It should be at AP level. But in WLC/AP setup, AP cannot operate without WLC’s brain. So port block need to occur at AP level, but WLC has to instruct AP what to do
HTH
Rasika
Hi Roshan,
1. WLC is the authenticator, So it will do the key generation & pass it to LAP. Refer below Cisco document which explain the process given below.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-1/Enterprise-Mobility-8-1-Design-Guide/Enterprise_Mobility_8-1_Deployment_Guide/cuwn.html
” An MSK is derived from the EAP authentication phase when WPA/WPA2 with 802.1X key management is used, or from the pre-shared key when WPA/WPA2 with PSK is used.
From the MSK, the client and WLC/AP derive the Pairwise Master Key (PMK).
Once these two Master Keys have been derived, the client and the WLC/AP initiate the 4-Way handshake with the Master Keys as the seeds to negotiate the actual encryption keys:
– Pairwise Transient Key (PTK) – The PTK is derived from the PMK and used in order to encrypt unicast frames with the client.
– Group Transient Key (GTK) – The Group Transient Key (GTK) is derived from the GMK, and is used in order to encrypt multicast/broadcast on this specific SSID/AP.”
PTK is include of multiple encryption keys. Every client sessions derive these keys for that session. GTK is used to encrpt broadcast/multicast packets.
HTH
Rasika
What is the difference between M2 “MIC” AND M3 “MIC”?
Both are same or different?
Hi Santhosh ,
M2 MIC and M3 MIC are different , in M3 , there will be added GTK & other information for MIC calculation . Hence MIC in M3 changes .
HTH ,
Sandy
What is the message sequence for renewal of PTK and GTK. Need to complete the 4-way handshake? Is there a way to just do PTK renewal and GTK renewal?
Thanks
what are the MIC parameters ? and is there any difference b/w wpa1 and wpa2 while performing 4 way hand shake
4. Transport the GTK & GTK sequence number from Authenticator to Supplicant & install them in Supplicant & AP(if not already installed)
is this correct?
If we enter correct password ,where the password used? Wethere used or not ? In which connection phase?
Hi Mohmmed,
4 Way handshake used to derive encryption keys.
In WPA2-Personal, you configure it on both client device & AP/WLC. So both sides use that as seed material to derive encryption keys.
In WPA2-Enterprise (802.1X), you do not have common password configured on your client & AP/WLC. Everytime client associate, they will derive keys dynamically.
HTH
Rasika
Hi Mohnmmed,
Just would like another aspect, the password entered by the client will be indirectly a decisive factor in calculating the MIC. as the password/passphrase is already available at the AP/WLC side; the MIC calculated at AP end should be same as calculated by client. There would be a mismatch when you have entered wrong password/passphrase, hence it would not move forward for M3.
Hi Mohammed ,
The passphrase which we enter in our device for connection , it will be mapped to PSK using Hash Algorithm .
Flow will be like this below :
Passphrase -> PSK -> PMK -> PTK ( again subdivided into KCK , KEK , TK )
Here PSK and PMK are hashed hexadecimal code
In Message 3, Authenticator use which cipher to encrypted GTK with PTK?
Yes, it will use PTK for encryption M3
Rasika
Thanks for your reply, but i wanna know which cipher it uses, like AES or DES?
AES cipher suite is used mainly. as TKIP is not used unless specified or configured.
Hi Sam ,
It may depend on the client’s security type connected to AP . If any one of the client’s has legacy Type security like (WEP/WPA1) , Legacy Client (Lowest Security type — Among WPA2 and WPA clients , WPA TKIP will be used for Group Cipher) Supported cipher will be used for encrypted broadcast/multicast traffic .
Hi Sandy,
That’s correct, One more add up here is the speed also dropped to 54Mbps as HT rates won’t be used if any one of connected clients not supporting WPA2. This is because the 11n amendment has requirement of WPA2 AES-CCMP support.
Hi
I´m a new bee here and trying to understand the debugs.
I´m trying to understand the user is using wpa or wpa 2 or wpa 3 from the given above captures, is there any possibilities to find out that from this captures?
In my setup we have wpa 2 + wpa 3 setup, for some apple users the M3 handshake is not happening.
The moment I enabled the WPA3 policy with PMK required, it started working.
if you look at RSN information element, it will tell what AKM suite being in use. That is the way to identify which methods in use.
WPA2-Enterprise (AKM 1 or 3)
WPA3-Enterprise (AKM 5,12 or 13)
WPA2- Personal (AKM 2,4 or 6)
WPA3-Personal (AKM 8 or 9)
Pls watch this webinar to better understand
HTH
Rasika
Hi
Very Nice Article.
I have some doubts on the PMK.
How is PMK shared to Authenticator and Supplicant ?
I mean what message/protocol.
Thanks.
With regards,
Ajay.
PMK is not shared between Authenticator (AP) & Supplicant (Client)
In WPA2-Personal, based on your passphrase configure (AP & Client) then independently derive PMK
In WPA2-Enterprise, Supplicant & RADIUS server mutually derive PMK (based on the public key exchange), then RADIUS server pass that onto Authenticator (WLC/AP)
HTH
Rasika
Thank you Rasika for your response. I was able to figure out eventually. Thanks again.
Nice Explanation.
Thank you Santhosh