Tags
H-REAP capable AP operates in these two different modes:
1. Connected mode: A H-REAP is said to be connected mode when its CAPWAP control plane link to WLC is up & operational.
2. Standalone mode: A H-REAP is said to be standalone when its CAPWAP link to WLC is down.
The Authentication mechanism used to authenticate a client can be Central or Local.
1. Central Authentication: Involved WLC in Central Office.
2. Local Authentication: Authentication does not involve WLC, handled by AP itself
The Switching mechanism used to switch a client can be Central or Local.
1. Central Switching : A WLAN on H-REAP is said to operate in “Central Switching” if data traffic of WLAN configured to tunnel back to WLC.
2. Local Switching : A WLAN on H-REAP is said to operate in “Local Switching” if data traffic terminate locally at the AP connected switchport itself.
** Only WLAN 1-8 can be configured for H-REAP Local Switching” **
Let’s see different modes available in this HREAP solution. Following topology diagram used for my testing. Even though ACS shown in the topology I have used WPA2-PSK for simplicity in this illustration. In a later post we will used ACS for authentication.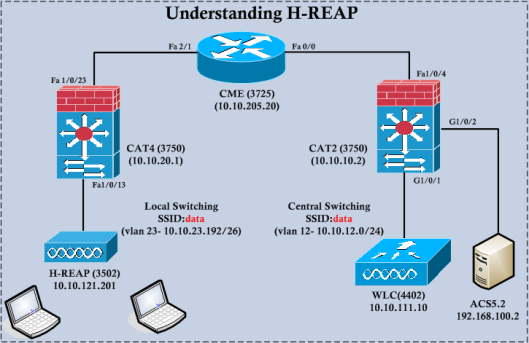
1. Central Authentication, Central Switching
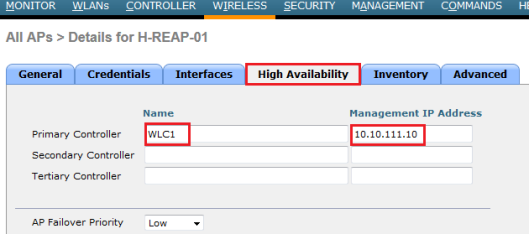
First you need to connect your AP into network (either from HQ or remote branch) & get it registered as local mode AP. Then select that AP & change the High Availability section to include HQ WLC name & IP in that section.
Then you have to change the AP mode into “H-REAP”. Once you do this AP will reboot automatically.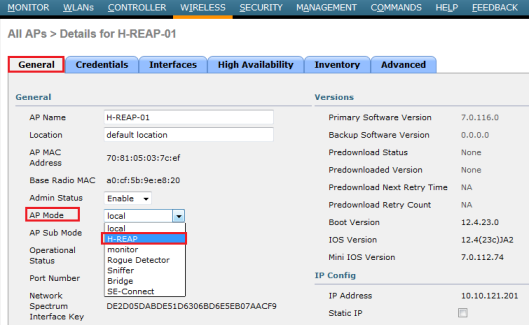
AP will be rebooted & join back to WLC in H-REAP mode
*Mar 1 00:13:18.119: %DHCP-6-ADDRESS_ASSIGN: Interface GigabitEthernet0 assigned DHCP address 10.10.121.201, mask 255.255.255.192, hostname H-REAP-01
*Mar 1 00:13:18.119: %LWAPP-3-LWAPP_INTERFACE_GOT_IP_ADDRESS: Interface GigabitEthernet0 obtained IP from DHCP...
*Mar 1 00:13:28.990: Logging LWAPP message to 255.255.255.255.
Translating "CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.mrn.com"...domain server (192.168.200.1)
*Mar 4 10:50:26.000: %CAPWAP-5-DTLSREQSEND: DTLS connection request sent peer_ip: 10.10.111.11 peer_port: 5246
*Mar 4 10:50:26.000: %CAPWAP-5-CHANGED: CAPWAP changed state to
*Mar 4 10:50:26.427: %CAPWAP-5-DTLSREQSUCC: DTLS connection created sucessfully peer_ip: 10.10.111.11 peer_port: 5246
*Mar 4 10:50:26.427: %CAPWAP-5-SENDJOIN: sending Join Request to 10.10.111.11
*Mar 4 10:50:26.427: %CAPWAP-5-CHANGED: CAPWAP changed state to JOIN
*Mar 4 10:50:26.541: %LWAPP-3-CLIENTEVENTLOG: No REAP co
wmmAC status is FALSEnfiguration file to load. Connect to controller to get configuration file
*Mar 4 10:50:26.541: %LWAPP-3-CLIENTEVENTLOG: No REAP configuration file to load. Connect to controller to get configuration file
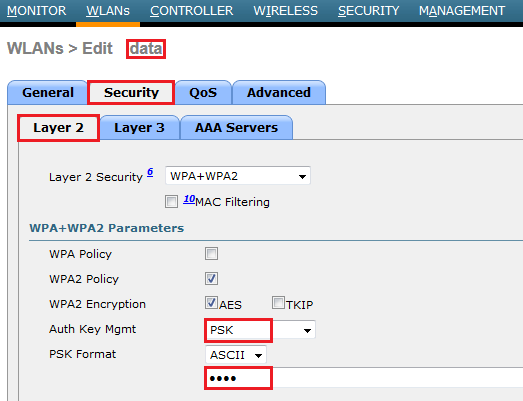
If your controller had few WLANs (ID less than 8) you can see them in remote office. I have used “data” & “guest” SSID created with WLAN ID#2 & 4 respectively. By default WLC will enforce H-REAP to use Central Authentication/Central Switching mode as H-REAP Local Auth & Local Switching is disabled by default for a given WLAN. (see below)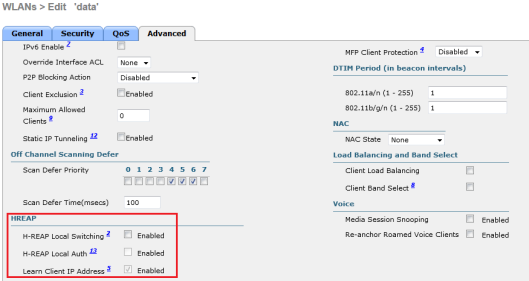
Since we are planning to use this SSID even when Central site is not reachable from Remote office, we have to use suitable authentication mechanism work even that kind of situation. So we have configured WPA2-PSK for this wlan.
You can test the connectivity via Anyconnect Client.
2. Authentication Down, Switching Down
If a WAN link goes down, this situation is known as “Authentication Down & Switching Down”. We will simulate this by shutting down the fa1/0/23 interface in CAT4. See below “debug capwap packets enable” output from WLC1.
(WLC1) >*osapiBsnTimer: Mar 10 05:23:44.597: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 Heartbeat timer expired for AP a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20
*spamReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.597: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 apfSpamProcessStateChangeInSpamContext: Down LWAPP event for AP a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 slot 1
*spamReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.599: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 Finding DTLS connection to delete for AP (10:10:121:201/14287)
*spamReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.599: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 Disconnecting DTLS Capwap-Ctrl session 0x136b72c8 for AP (10:10:121:201/14287)
*spamReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.599: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 CAPWAP State: Dtls tear down
*spamReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.600: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 DTLS connection closed event receivedserver (10:10:111:11/5246) client (10:10:121:201/14287)
*spamReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.600: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 Entry exists for AP (10:10:121:201/14287)
*spamReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.601: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 apfSpamProcessStateChangeInSpamContext: Deregister LWAPP event for AP a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 slot 0
*spamReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.601: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 apfSpamProcessStateChangeInSpamContext: Deregister LWAPP event for AP a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 slot 1
*apfReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.603: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 Received LWAPP Down event for AP a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 slot 1!
*apfReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.605: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 Deregister LWAPP event for AP a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 slot 0
*apfReceiveTask: Mar 10 05:23:44.605: a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 Deregister LWAPP event for AP a0:cf:5b:9e:e8:20 slot 1
Previously this WLAN was centrally authenticated & centrally switched, both control & data traffic were tunneled back to WLC. Therefore without WLC, the client is unable to maintain association with the H-REAP and it is disconnected. This state of HREAP with both client association & authentication being down is referred to as “Authentication Down, Switching Down”.
3. Central Authentication , Local Switching
Prior to test Local Switching we will create a local switched vlan (10.10.23.192/26) in CAT4. Also define DHCP pool on the same switch.
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.23.193 10.10.23.200 ip dhcp pool VLAN23 network 10.10.23.192 255.255.255.192 default-router 10.10.23.193 domain-name mrn.com ! interface Vlan23 ip address 10.10.23.193 255.255.255.192 ip pim sparse-mode
Next step is to change the “data” WLAN to do local switching for HREAP. You need tick “H-REAP Local Switching” check box as shown below. It will automatically tick “Learn Client IP Address” box as well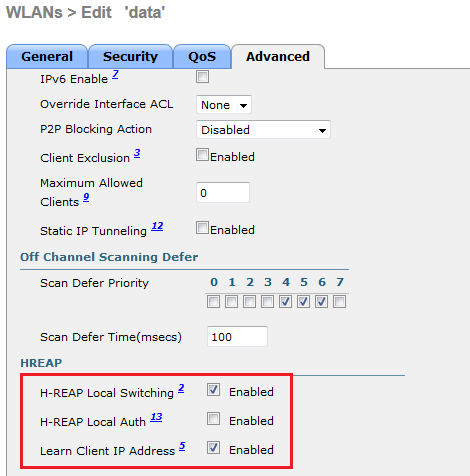
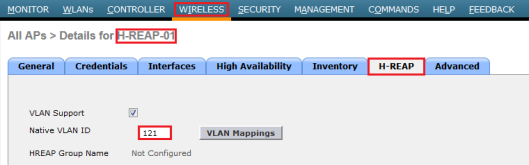
Then go to “H-REAP” tab & assign the local vlan for H-REAP local switching. keep in mind you have to correctly set native vlan which would be the vlan H-REAP mgt IP reside. In my case Vlan 121 will set as native vlan as my HREAP got that subnet IP.
interface FastEthernet1/0/13
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport trunk native vlan 121
switchport mode trunk
end
Once you click “Vlan Mapping” you can add vlans that you want to do local switching. In my case I have added vlan 23.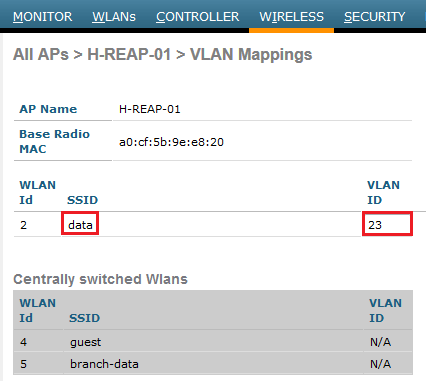
Now you can test the connectivity using AnyConnect client. You should see you will get an IP from this local switched subnet.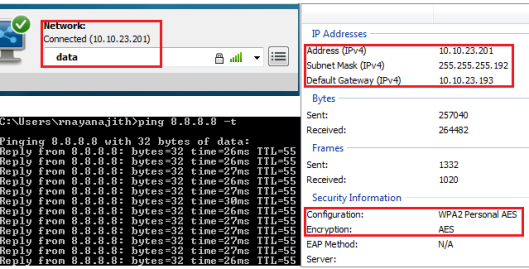
In this case even we shutdown the WLC connected switchport, client remain connected & work normally. But if a new client try to associate it will fail because of WLC down & we use central authentication. As you can see below previously associated client work without any problem. But for a new client did not get authenticated.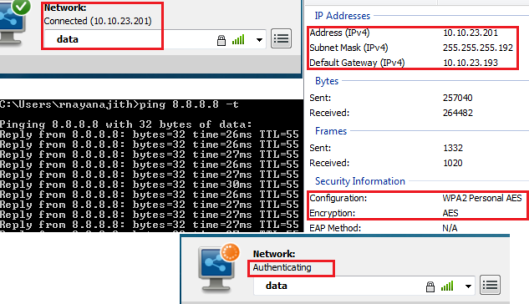
4. Local Authentication , Local Switching
Next, we will enable Local Authentication where it will allow to H-REAP to authenticate clients even when central controller is not reachable (or WAN link is down). You have to go to “data” WLAN Advanced Settings & tick ” H-REAP Local Authentication” as shown in the below.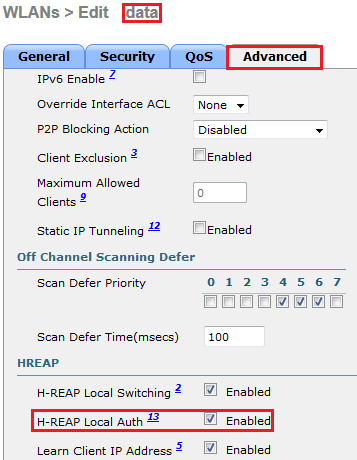
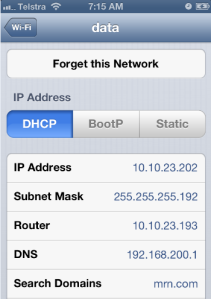
In this situation even WLC is not reachable, still new clients in the branch office able to authenticate & use the network. I have used my iPhone to connect to “data” WLAN while WLC is down. As shown below I have authenticated successfully & got vlan 23 IP.
If you look at H-REAP console you should see something like this which indicate it has lost connectivity to WLC & put into “Discovery” mode.
*Mar 9 20:10:22.578: %LWAPP-3-CLIENTEVENTLOG: Switching to Standalone mode *Mar 9 20:10:22.631: %DTLS-5-SEND_ALERT: Send FATAL : Close notify Alert to 10.10.111.11:5246 *Mar 9 20:10:22.685: %WIDS-5-DISABLED: IDS Signature is removed and disabled. *Mar 9 20:10:22.688: %CAPWAP-5-CHANGED: CAPWAP changed state to DISCOVERY
You can use “show capwap reap association” CLI command on H-REAP to verify client association/authentication.
H-REAP-01#show capwap reap associat Address : 04f7.e4ea.5b66 Name : NONE IP Address : 10.10.23.202 Interface : Dot11Radio 1 Device : unknown Software Version : NONE CCX Version : NONE Client MFP : Off State : Assoc Parent : self SSID : data WLAN : 2 Hops to Infra : 1 Association Id : 2 Clients Associated: 0 Repeaters associated: 0 Tunnel Address : 0.0.0.0 Key Mgmt type : WPAv2 PSK Encryption : AES-CCMP Current Rate : m6. Capability : WMM Supported Rates : 24.0 36.0 48.0 54.0 m0. m1. m2. m3. m4. m5. m6. m7. Voice Rates : disabled Bandwidth : 20 MHz Signal Strength : -58 dBm Connected for : 27 seconds Signal to Noise : 37 dB Activity Timeout : 300 seconds Power-save : On Last Activity : 0 seconds ago Apsd DE AC(s) : NONE Packets Input : 272 Packets Output : 72 Bytes Input : 22928 Bytes Output : 21243 Duplicates Rcvd : 0 Data Retries : 16 Decrypt Failed : 0 RTS Retries : 0 MIC Failed : 0 MIC Missing : 0 Packets Redirected: 0 Redirect Filtered: 0 Session timeout : 86400 seconds Reauthenticate in : 86371 seconds REAP Data Switching: Local Address : a088.b435.c2f0 Name : H-REAP-01 IP Address : 10.10.23.201 Interface : Dot11Radio 1 Device : ccx-client Software Version : NONE CCX Version : 4 Client MFP : Off State : Assoc Parent : self SSID : data WLAN : 2 Hops to Infra : 1 Association Id : 1 Clients Associated: 0 Repeaters associated: 0 Tunnel Address : 0.0.0.0 Key Mgmt type : WPAv2 PSK Encryption : AES-CCMP Current Rate : m15. Capability : WMM Supported Rates : 24.0 36.0 48.0 54.0 m0. m1. m2. m3. m4. m5. m6. m7. m8. m9. m10. m11. m12. m13. m14. m15. Voice Rates : disabled Bandwidth : 20 MHz Signal Strength : -53 dBm Connected for : 860 seconds Signal to Noise : 44 dB Activity Timeout : 299 seconds Power-save : Off Last Activity : 1 seconds ago Apsd DE AC(s) : NONE Packets Input : 11717 Packets Output : 8090 Bytes Input : 2221176 Bytes Output : 3193050 Duplicates Rcvd : 5 Data Retries : 237 Decrypt Failed : 0 RTS Retries : 0 MIC Failed : 0 MIC Missing : 0 Packets Redirected: 0 Redirect Filtered: 0 Session timeout : 86400 seconds Reauthenticate in : 85538 seconds REAP Data Switching: Local SSID: data on Dot11Radio1 bssid: a0cf.5b9e.e82e Mode: 0x192, WLAN: 2 , VLAN name: 002 VLAN ID: 23 Key Mgmt 12, Reap flags 0x1, Guest Yes, Current Users 2, Open Auth SSID: data on Dot11Radio0 bssid: 0000.0000.0000 Mode: 0x192, WLAN: 2 , VLAN name: 002 VLAN ID: 23 Key Mgmt 12, Reap flags 0x1, Guest Yes, Current Users 0, Open Auth
In a future post we will see H-REAP local switching/local Authentication with ACS5.2 (Authenticating with EAP methods).
I have followed cisco “H-REAP Modes of Operation Configuration Example” for this post(Doc ID 81680). Please read that as well for better understanding this topic.
Related Posts
1. Office Extend – Overview
2. Configuring OEAP
3. How does OEAP work ?
4. H-REAP with RADIUS
5. OEAP with Multiple Remote LANs

Thank you for your excellent post. I learn a great deal from it. If you don’t mind,
I would like to ask you a question though. In local switching mode, why does the connected client have the ip address in vlan23 rather than native vlan121? Many documents I came across mentioned that the client get ip in native vlan subnet, just as the HREAP AP does.
Thanks and good luck in your CCIEW exam.
Hi Dave,
Thanks for wishes for my exam…
If you want to have multiple vlans in Branch office which needs to work in local switching mode you can do that by vlan mapping. In this situation only H-REAP mgt IP should be in native vlan & clients can be in any other vlan (but keep in mind H-REAP connected switch port to configure as Trunk Port). Not sure which WLC software version this added. I am on 7.0.116 code & its there.
Since WAN link failure situations client should have local vlan (otherwise client cannot reach its gateway) in order to work. That’s why I create vlan 23 (but same SSID) for local switching purpose.
Hope this clear.
Rasika
“Only WLAN 1-8 can be configured for H-REAP Local Switching”.
I have tested on WLC with 7.0.220.0 firmware and didn’t encounter any issue with wlan which id was number 12.
I made trafic tests and the local switching was working fine.
Was I lucky or has the limitation been removed ?
I am unable to find the answer in release notes or elsewhere.
Hi Rasika,
In my tests i see that in Central-Authentication/Local switching state when the link is down and AP is in Standalone mode,new clients that use PSK key are able to connect.They are rejected only if they use WPA Ent, which involves local or external radius.
In your case the client using PSK couldn’t connect.
Regards.
If it is central authentication & local switching, when WAN link is down, new client authentication should be failed. Not sure how it worked for you….It is interesting if it is the case with this software code.
pls do more testing & confirm…
Rasika
Layer 2 wireless data encryption is always handled at the access point level so this would explain why it worked.
Take a look here..
https://supportforums.cisco.com/message/3506698#3506698
Regards.
Yes, good pickup & I was wrong on that. Thanks for the reference link
Rasika
You welcome Ras.
Regards.
Hi Rasika,
For a new site having:
– freshly installed virtual_WLC (datasheet states it is not compatible with local-mode AP)
– out of the box 1600 series AP
How can I setup each AP to FlexConnect mode (I read that each AP should firstly connect in local-mode to the WLC)?
Yes, you can register them in local mode & then you can go to each AP & change the mode to FlexConnect
But the documentation says that virtual WLC does not support local-mode AP.
Is the registration going to work?
Yes, Registration will work, but you will not able to advertise SSID unless you convert it to FlexConnect.
HTH
Rasika
Thank you for your excellent post. now i am undestand how ip address is assigned to user on remote location. Thank you very much.
No worries Dilip, Good to see it helps you
Rasika
One problem I came across was the remote APs themselves losing association to the controller after a WAN/VPN outage. It was difficult to reliably reproduce, but under Wireless -> Access Points -> Global Configuration I did find some settings related to heartbeats, and am wondering if enabling them would fix the issue.
AP Restransmit count is the one you can tweak, increase it to 8 (default 5) & see if that make any difference
HTH
Rasika
Thanks for the reply. Cisco TAC recommend using DHCP option 43. This surprised me because I thought this was obsolete, but it did completely solve the problem. We’re still using an old 4400 series controller with 1142 APs.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wireless-mobility/wireless-lan-wlan/97066-dhcp-option-43-00.html
Though it is strange suggestion, good to see that fix your issue 🙂
Rasika
Hi Rasika,
Is it possible to have the configuration as follow :
central switching for the wireless traffic and local authentication (because there is a radius server at the branch location). ?
Hi Florian,
Purpose of FlexConnect/H-REAP is to preserve WAN bandwidth & make traffic flow optimum. Hence FlexConnect local switching feature.
With FlexConnect, you can use central switching, if you want to use RADIUS server in branch for that SSID, you can, but traffic flow point of view it is not optimum (As client auth, first hit WLC, then WLC send to RADIUS sit on branch)
HTH
Rasika
Hi Rasika,
I have a Flexconenct AP working on Central Authentication, Local Switching and using WPA2-PSK authentication. Could you tell me what will be the impact if the WLC goes down.
“Only WLAN 1-8 can be configured for H-REAP Local Switching”.
is this still applicable with newer AireOS?
Will appreciate quick response.